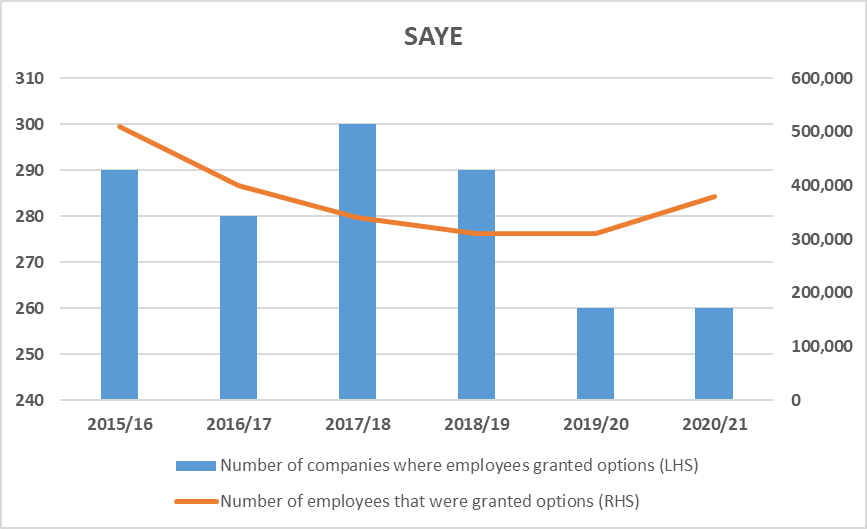
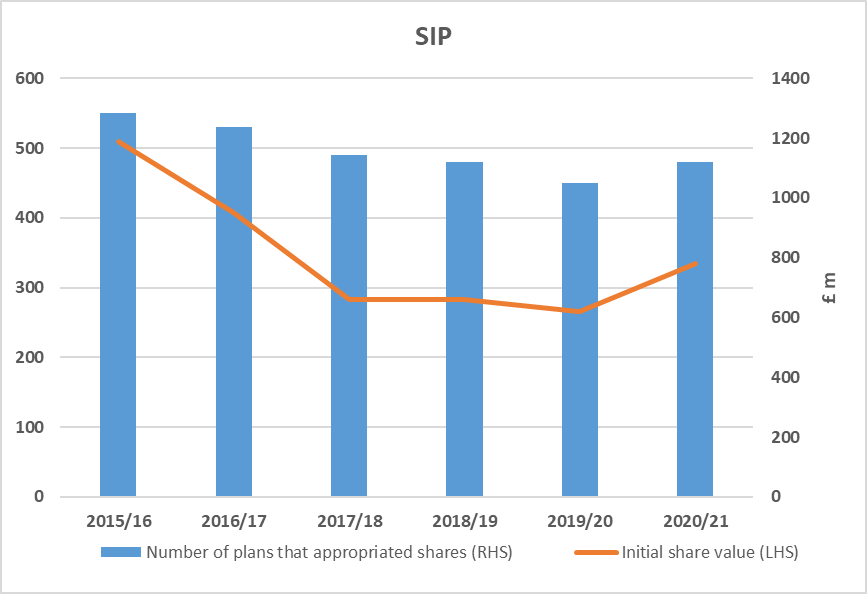
All the recent changes being implemented to solve the NHS pensions problems.
Whilst there were no new pensions related announcements in the NHS Long Term Workforce Plan published on 30 June, it did make reference to some of the changes that are already in plan. These, along with the pensions tax changes announced in the March 2023 Budget, have seen a significant shift towards resolving many of the key issues facing high earnings members of the NHS pension scheme.
A key stated motive for the increase in the annual allowance and the removal of the lifetime allowance (LTA) announced in the March 2023 Budget was to aid staff retention within the NHS.
The abolition of the LTA resolves one of these issues entirely. Members can now build up as much pension as possible without fear of an LTA charge. The change removes a significant disincentive to continue working.
However, the annual allowance was often the bigger issue. The increase from £40,000 to £60,000 will help with the problem and ensure many consultants and GPs will not have to face regular annual allowance charges. There are still likely to be spikes in pension inputs above the annual limit caused by things such as the way NHS pay scales reward length of service, and whenever they take on additional pensionable responsibilities. However, the higher annual allowance, coupled with, as time goes by, potentially more carry forward being available, should mean that annual allowance excesses are far less frequent.
For very high earners there is still the issue of tapering. However, the increase in the Adjusted Income limit will move more NHS workers out of scope. Many NHS workers in this bracket are likely to have an element of private earnings and, in many cases, can control their level of taxable income by using limited companies to perform their private duties.
As well as the increase in the annual allowance there were also a couple of technical changes to the way the pension inputs will be calculated, which aim to further reduce potential annual allowance issues.
The first applies to all public sector pension schemes and will allow negative inputs in a legacy final salary section of the scheme to be offset against the pension inputs in the career average section. Negative inputs can occur where the inflation rate used in the pension input calculation exceeds the annual increase in the pay or revaluation rate used for calculating the final salary benefits.
The second change intends to correct the fact that there is a disconnect between the inflationary offset used in the tax calculations for the pension input calculation and the one used to revalue benefits in the schemes. Without the amendment, the steep rise in inflation would have created some very high pension inputs, which are arguably unfair as the pension input is only supposed to represent the increase in benefits above inflation.
To resolve this, the effective date of the revaluation of Career Average Revalued Earnings (CARE) schemes was moved from 1 April to 6 April with effect from 6 April 2023. For the 1995 scheme and 2008 schemes the date used to revalue lifetime earnings, i.e. the ‘dynamizing factors’, was also moved from 1 April to 6 April. The change to the CARE scheme will impact all members, whereas the change to the older schemes only applies to practitioner earnings. The changes have the effect of aligning the CPI values. This will also mean that the inflationary part of the pension ‘growth’ will now move into the next tax year. So, rather than the increase being reflected in a 2022/23 pension input it will now move to the 2023/24 tax year.
Tax year 2022/23 will be a transitional year which means, effectively, there will be no revaluation element within the calculations and, so, this should mean lower pension inputs.
Note, however, there is no change to the calculation for non-practitioner members in the final salary sections of the scheme. The pension inputs will still be based on any increases in their final salary between the start and the end of the pension input periods.
In addition to the tax related changes, new retirement flexibilities have been introduced as a further part of the plan to aid staff retention by offering options that will remove some of the issues within the 1995 section of the scheme that appear to encourage employees to retire early.
From April 2023 – retire and re-join
Under the previous rules, members who took their 1995 benefits were not allowed to build up any further pension in the 2015 scheme. Any further work had to be on a non-pensionable basis.
Members can now retire and take their full benefits from the 1995 scheme, then return to work after a break of at least 24 hours. They can then re-join the 2015 scheme and continue to build up benefits.
This is an important change because there are no late retirement factors in the 1995 scheme and, so, no incentive to continue in the 1995 scheme beyond age 60. Many employees therefore chose to retire at 60. The change removes a key disincentive to work beyond age 60.
However, it will mean those taking their 1995 pension benefits will be subject to high marginal rates of income tax if they are taken before they are actually needed where the member continues in employment.
The previous restriction for ‘retire and return’ workers meant members of the 1995 scheme were limited to working 16 hours a week for the first month after re-employment. This restriction is now removed, and members simply need to take a 24-hour break and can then start building 2015 benefits immediately. Members will, however, be required to enter a new contract of employment. Whilst this will need to be agreed locally with their employer, the Government stated that it would “strongly encourage employers to offer staff the same terms and conditions on this new contract should they decide to retire and return”.
From October 2023 – partial retirement
This new option allows those who have reached the normal minimum retirement age to take between 20% and 100% of their 1995 pension benefits in one or two stages without having to leave their job. They can take the benefits from the 1995 scheme, continue to work and build up benefits in the 2015 scheme.
To take advantage of this option, employees must reduce their pensionable pay by at least 10%. GPs and other practitioners must reduce their NHS commitments by at least 10%.
Where benefits are taken before the normal pension age for the scheme (age 60 for most, but 55 for certain occupations) the usual early retirement reduction factors will apply.
Comment
The full package of measures undoubtedly improves the position for high earners in the NHS pension scheme. The significant improvement in the tax position along with the additional retirement flexibilities are welcomed and should provide some help with staff retention. The ability to take benefits from the 1995 section of the scheme and continue to accrue benefits in the 2015 scheme without fear of an LTA charge removes a strong incentive to retire at age 60.
This is an example of one of the recent news bulletins that was posted on our Techlink website. Signing up to Techlink will give you access to original articles, like this, on a daily basis. Techlink also provides you with a comprehensive (and searchable) library of information, daily bulletins on developments of relevance to the industry, multimedia learning and professional development tools. Techlink can also be your ‘gateway’ for accessing consultancy through our ‘ASK’ service which enables you to receive responses to your technical questions from our highly trained technical consultants.
You can sign up for a free 30 day trial of Techlink at anytime. For more information go to www.techlink.co.uk